
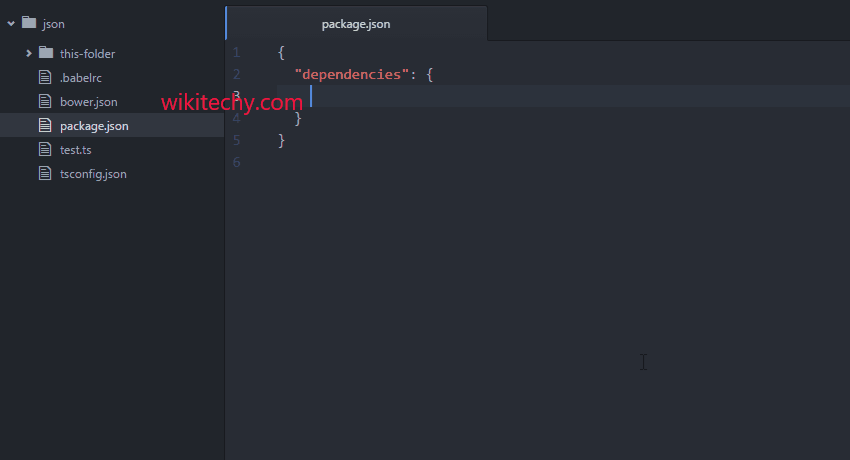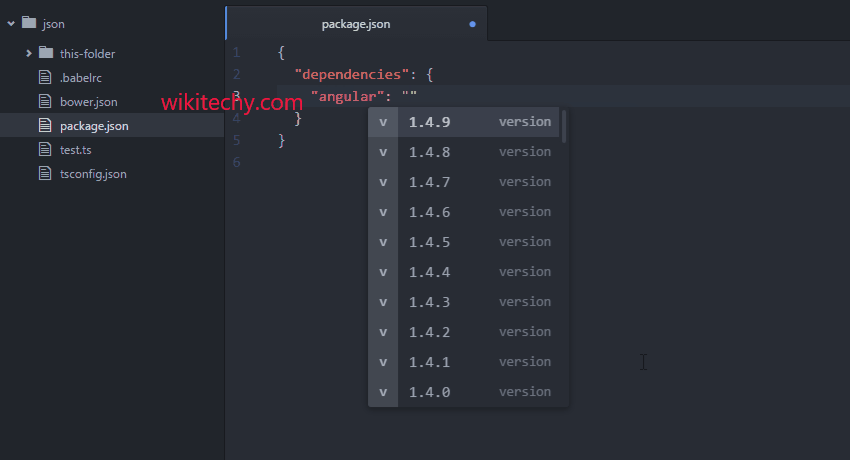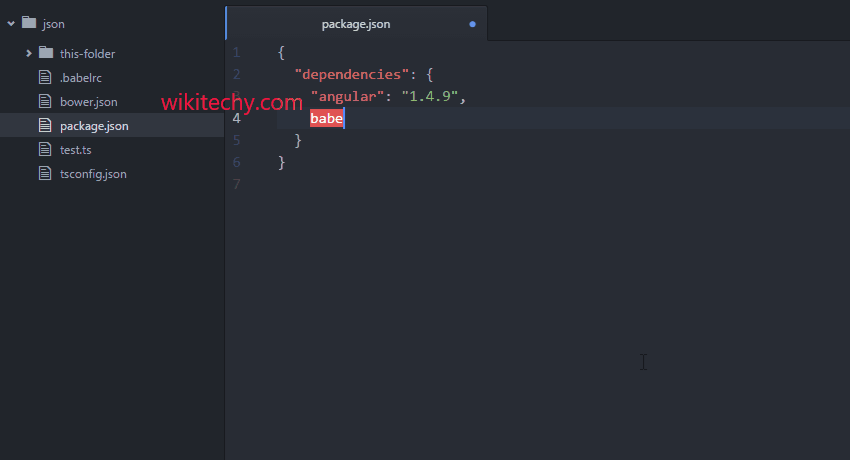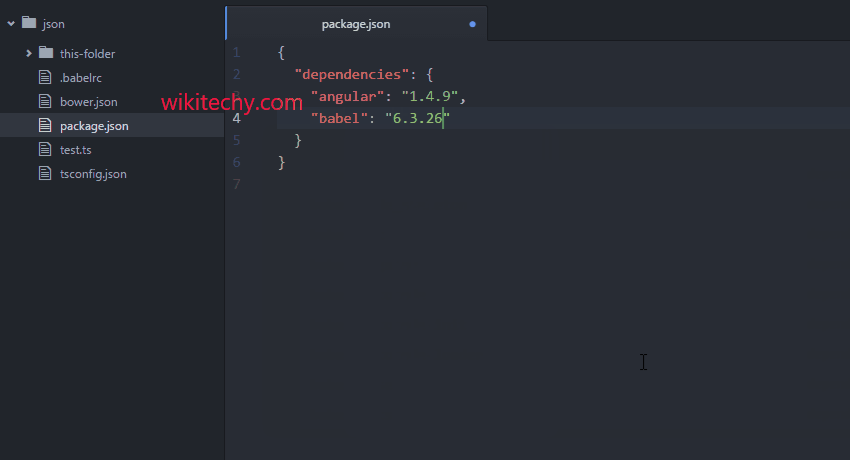
package mainįmt.Println(l, "bytes written successfully") One of the most common file writing operations is writing a string to a file. Please run all the programs of this tutorial in your local system as playground doesn't support file operations. We will also learn how to write to a file concurrently.

In this tutorial, we will learn how to write data to files using Go. It's important to note that these functions permanently delete the files or directories, so we need to careful when using them.Welcome to tutorial no. # delete "mydir" directory and all of its contents In order to remove a non-empty directory, we can use the rmtree() method inside the shutil module. Now let's use rmdir() to delete an empty directory, import os

Here, we have used the remove() method to remove the "myfile.txt" file. In Python, we can use the remove() method or the rmdir() method to remove a file or directory.įirst let's use remove() to delete a file, import os Here, 'test' directory is renamed to 'new_one' using the rename() method. The rename() method can rename a directory or a file.įor renaming any directory or file, rename() takes in two basic arguments:

If the full path is not specified, the new directory is created in the current working directory. This method takes in the path of the new directory. In Python, we can make a new directory using the mkdir() method. If no path is specified, it returns the list of subdirectories and files from the current working directory. This method takes in a path and returns a list of subdirectories and files in that path. Here, we have used the chdir() method to change the current working directory and passed a new path as a string to chdir().Īll files and sub-directories inside a directory can be retrieved using the listdir() method. And we can use both the forward-slash / or the backward-slash \ to separate the path elements. The new path that we want to change into must be supplied as a string to this method. In Python, we can change the current working directory by using the chdir() method. Here, getcwd() returns the current directory in the form of a string. This method returns the current working directory in the form of a string. We can get the present working directory using the getcwd() method of the os module. Python has the os module that provides us with many useful methods to work with directories (and files as well). A directory inside a directory is known as a subdirectory. A directory is a collection of files and subdirectories.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
